

 |
||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||
| The Use of Salt in Aquaculture | ||||||
| Page 3 of 5 | Pages: 1 . 2 . 3 . 4 . 5 | |||||
THE USE OF SALT TO PREVENT AND TREAT BROWN BLOOD DISEASE Freshwater fish, particularly channel catfish, are susceptible to brown blood disease, which is caused by an accumulation of nitrite (N0 2 ) in the water. Although most studies conducted on brown blood disease have used channel catfish as a model, many other freshwater species are also susceptible to the condition. A detailed discussion of nitrite toxicity is provided in a separate IFAS publication. Following is a brief review of the use of salt to prevent and treat brown blood disease. In freshwater systems, nitrite toxicity is directly related to chloride (Cl - ) concentration, since nitrite (N0 2 - ) and chloride (Cl - ) particles compete for space to cross the gills and enter the bloodstream (see Figure 1 ). As chloride concentration in the water increases, nitrite's ability to enter the bloodstream decreases. 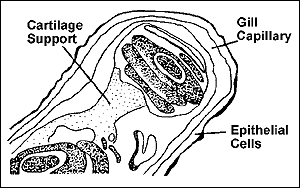
Figure 1 The critical component in brown blood disease is the chloride (Cl - ) portion of the salt molecule (NaCl). For this reason, a test to measure chloride concentration (ppm) should be used rather than a test that uses a hydrometer or refractometer to measure salinity. A minimum chloride concentration of 20 ppm is recommended to prevent nitrite toxicity among channel catfish in ponds. Most ponds are supplied with water containing at least 20 ppm Cl - ; however, salt should be added to ponds containing less than 20 ppm Cl - to increase the chloride concentration to the desired level (see Table 1 ). For each acre-foot of water in the pond (1 surface acre, 1 foot deep = 43,560 ft 3 ), 4.5 pounds of salt adds 1 ppm chloride. Salt may be used to minimize mortality and facilitate recovery of fish that develop brown blood disease. For every ppm of nitrite present, 6 ppm chloride should be used to control the disease. As described earlier, the producer must determine the required chloride concentration, adding 4.5 pounds of salt per acre-foot of water for each ppm Cl - needed (see Table 2 ). more ... |
 |
|||||
| About Us :: Message Board :: Chat | |||||
| Library :: Photo Gallery :: Links & Resources :: Breeders & Sponsors :: Merchandise | |||||
| Website designed by: EthanCote.com | © 2001-2004, SimplyDiscus.com. All Rights Reserved. | ||||