

 |
||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||
| Introduction to Freshwater Fish Parasites | ||||||
| Page 4 of 14 | Pages: 1 . 2 . 3 . 4 . 5 . 6 . 7 . 8 . 9 . 10 . 11 . 12 . 13 . 14 | |||||
Ambiphyra Ambiphyra, previously called Scyphidia, is a sedentary ciliate that is found on the skin, fins, or gills of host fish. Its cylindrical shape, row of oral cilia, and middle bank of cilia identify Ambiphyra ( Figure 6 ). 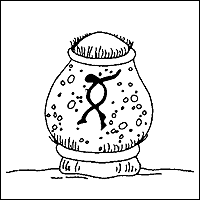 Figure 6: An illustration of a Ambiphyra cilatiate.
Figure 6: An illustration of a Ambiphyra cilatiate.
It is common on pond-reared fish, and when present in low numbers (less than five organisms per low power field), it is not a problem. High organic loads and deterioration of water quality are often associated with heavy, debilitating Ambiphyra infestations. This parasite can be controlled with one application of any of the treatments listed in Table 1. Apiosoma Apiosoma, formerly known as Glossatella, is another sedentary ciliate common on pond-reared fish. Apiosoma can cause disease if their numbers become excessive. The organism can be found on gills, skin, or fins. The vase-like shape and oral cilia are characteristic ( Figure 7 ).  Figure 7: An illustration of a Apiosoma ciliate.
Figure 7: An illustration of a Apiosoma ciliate.
Apiosoma can be controlled with one application of one of the treatments from Table 1 . Epistylis Epistylis is a stalked ciliate that attaches to the skin or fins of the host. Epistylis is of greater concern than many of the ciliates because it is believed to secrete proteolytic ("protein-eating") enzymes that create a wound, suitable for bacterial invasion, at the attachment site. 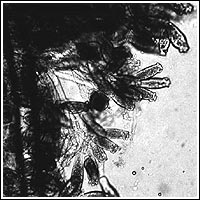 Figure 8: A microscopic view of the stalked ciliate.
Figure 8: A microscopic view of the stalked ciliate.
It is similar in appearance to Apiosoma except for the non-contractile long stalk ( Figure 8 ) and its ability to form colonies. In contrast to the other ciliates discussed above, the preferred treatment for Epistylis is salt. Fish can be placed into a 0.02% salt solution as an indefinite bath, or a 3% salt dip. More than one treatment may be required to control the problem. For more information, see IFAS Extension Fact Sheet VM-85 , "Red Sore Disease" in Game Fish . Capriniana Capriniana, historically called Trichophyra, is a sessile ciliate that attaches to the host's gills with a sucker. They have characteristic cilia attached to an amorphous-shaped body ( Figure 9 ). In heavy infestations, Capriniana can cause respiratory distress in the host. One treatment from a chemical listed in Table 1 should be adequate. 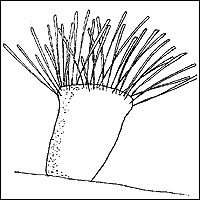 Figure 9: An illustration of a sessile ciliate.
Figure 9: An illustration of a sessile ciliate.
more ... |
 |
|||||
| About Us :: Message Board :: Chat | |||||
| Library :: Photo Gallery :: Links & Resources :: Breeders & Sponsors :: Merchandise | |||||
| Website designed by: EthanCote.com | © 2001-2004, SimplyDiscus.com. All Rights Reserved. | ||||