

 |
||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||
| Introduction to Freshwater Fish Parasites | ||||||
| Page 8 of 14 | Pages: 1 . 2 . 3 . 4 . 5 . 6 . 7 . 8 . 9 . 10 . 11 . 12 . 13 . 14 | |||||
Microsporidia Microsporidians are intracellular parasites that require host tissue for reproduction. Fish acquire the parasite by ingesting infective spores from infected fish or food. Replication within spores (schizogony) causes enlargement of host cells (hypertrophy). Infected fish may develop small tumor-like masses in various tissues. Diagnosis is confirmed by finding spores in affected tissues, either in wet mount preparations, or in histologic sections. Clinical signs depend on the tissue infected and can range from no visible lesions to mortalities. In the most serious cases, cysts enlarge to a point that organ function is impaired and severe morbidity and/or mortality results. A common microsporidian infection is Pleistophora , which infects skeletal muscle ( Figure15 ). 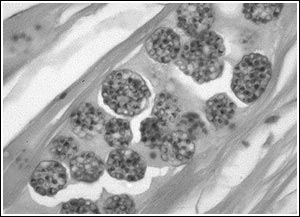 Figure 15: A magnified view of an infected skeletal muscle with Pleistophora.
Figure 15: A magnified view of an infected skeletal muscle with Pleistophora.
There is no treatment for microsporidian infections in fish. Spores are highly resistant to environmental conditions and can survive for long periods. Elimination of the infected stock and disinfection of the environment is recommended. Coccidia Coccidia are intracellular parasites described in a variety of wild-caught and cultured fish ( Figure 16 ). Their role in the disease process is poorly understood, but there is increasing evidence that they are potential pathogens. The most common species encountered in fish are intestinal infections. Inflammation and death of the tissue can occur, which can affect organ function. Other infection sites include reproductive organs, liver, spleen, and swim bladder. 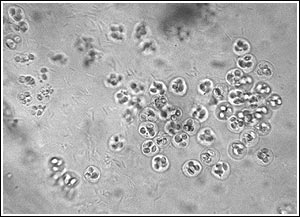 Figure 16: A magnified view of Coccidia.
Figure 16: A magnified view of Coccidia.
Clinical signs depend on target organ affected but may include general malaise, poor reproductive capacity, and chronic weight loss. A definitive diagnosis of tissue Coccidia should be completed with histologic or electron microscopy. Several compounds have been used to control coccidiosis with some success; however, consultation with an experienced fish health professional is recommended. Maintaining a proper environment and reducing stress appear to be important in preventing Coccidia outbreaks in cultured fish. more ... |
 |
|||||
| About Us :: Message Board :: Chat | |||||
| Library :: Photo Gallery :: Links & Resources :: Breeders & Sponsors :: Merchandise | |||||
| Website designed by: EthanCote.com | © 2001-2004, SimplyDiscus.com. All Rights Reserved. | ||||